Vernon Smith, Nobel prize winner 2002, and Bart Wilson are renowned experimental economists. They faced an apparent contradiction when neoclassical utility maximization or Max-U model, that explained perfectly well supply-and-demand market experiments, failed in two-person games. Behavioral and experimental economists explained the differences ex-post as "social preferences".
Humanomics is a neologism in reference to the study of the human problem as both personal social and impersonal economic.
Morality is an emergent order based on the will of the people to seek praise and praiseworthiness and avoid blame and blameworthiness. "In Adam Smith's model of human social conduct, actions are governed by context-dependent rules based on experience and human capacity for mutual sympathetic fellow-feeling". In other words, humans have the capacity to extract the accepted rules by observing and feeling others around.
None of the authors, including Adam Smith, are experts on play but it is striking how they recognize and fit the role of play in children to understand the moral rule set.
None of the authors, including Adam Smith, are experts on play but it is striking how they recognize and fit the role of play in children to understand the moral rule set.
"The child naturally wishes to gain their favour, and to avoid their hatred or contempt... and it soon finds that it can do so in no other way than by moderating, not only its anger, but all its other passions, to the degree which its play-fellows and companions are likely to be pleased with."
The capacity to understand the moral rules is context free but the rules in themselves are context relevant. Societies flourish when that mutual support is provided in the reciprocity of gratitud and friendship bound together in good offices of affection and esteem". Societies thrive when their rules promote cooperation, exchange and mutual respect.
One key takeaway from Humanomics is that human behavior follows some general rules on how rules are set, yet the specific rules are different based on time and context. Therefore, we can't use the same rule set to evaluate two different results. But we can identify some common denominators in functional system vs dysfunctional ones.
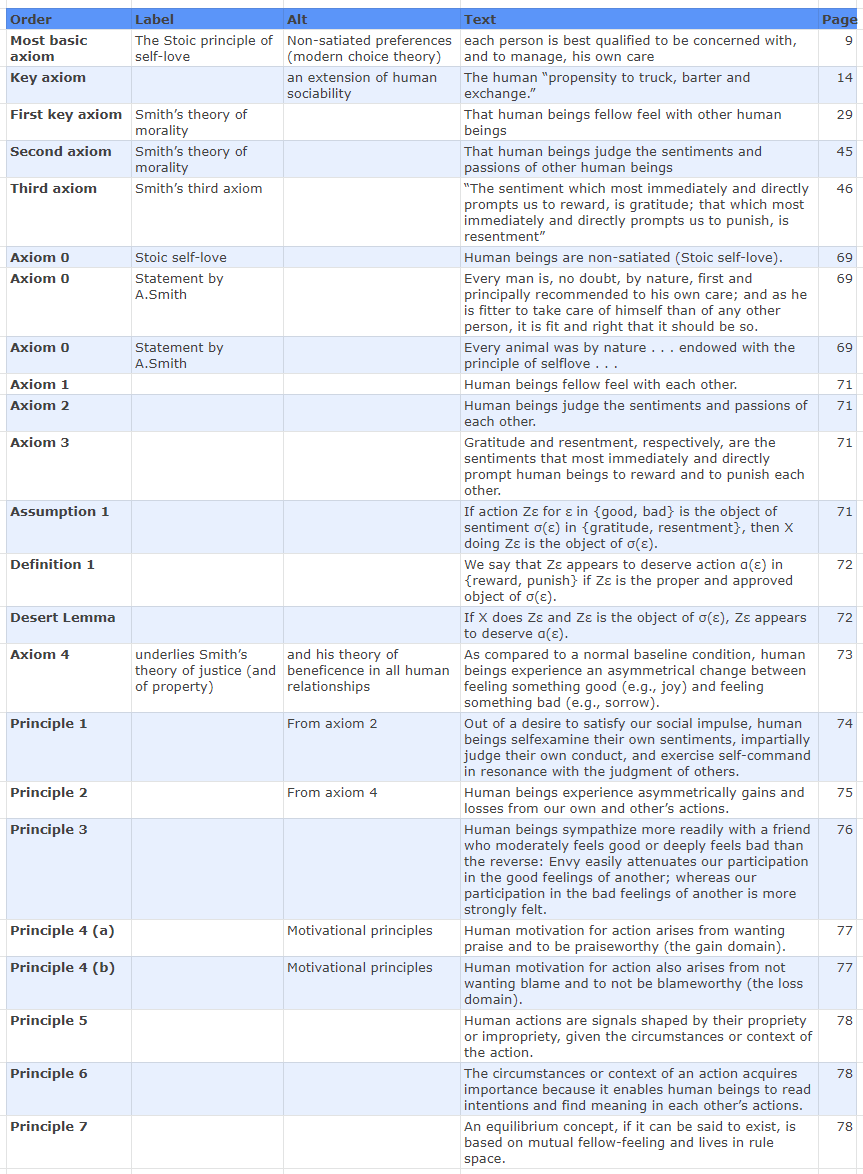
"When dealing with human beings, we must get comfortable with the imprecision of our humanity"Smith and Wilson coded Adam Smith's ideas in a series of Axioms and Principles, summarized by Leonel Morales, "One aim in restating Smith's propositions as we do is to spell out the simplicity and universality with which he can be read".
Smith and Wilson proceed to analyze some classical games and see how these axioms and principles can explain the results, opposite to the failure of Max-U and behavioral economics. Finally they use Adam Smith's theory to predict the outcome of a new set of games.
For the authors Adam Smith Theory of Moral Sentiments is a better model to explain how people interact. The analysis also closes the apparent gap between the Theory of Moral Sentiments and the Wealth of Nations.
"His project in Sentiments is to address how moral conduct emerges out of human interactive experience to form a system of general rules that wisely order society. In Wealth he extends that system to markets and national economy to enable a better understanding of the sources and evolution of the economic order."

No comments:
Post a Comment